|
9/23/2018 0 Comments How to Write Special Education Achievement Reports - with Reading Evaluation Examples!
So you finished testing a student. Now what?
Most testing programs have taken some of the workload off of your shoulders! The majority of achievement tests have moved to web-based scoring. Testers are able to plug in raw scores, click a button or two, and get furnished with standard scores and various reports able to do some of the analysis for you. Writing testing reports can feel overwhelming. The information shared within a testing report is conveyed to families and educators working with the student. The data should be utilized during the educational planning process.
Every testing report should begin by stating the reason for testing. Has the student been referred for testing due to a recent diagnosis? Has the student been struggling in the area of reading? Is the referral the result of a student/teacher assistance team meeting? Is the testing the result of a three-year re-evaluation per a student’s IEP?
Next, the tests administered should be listed.
A student’s background information should be summarized as well. What information is relevant for this evaluation? Did a student repeat a grade? Has the student had extended absences from school? Is the student a second-language learner?
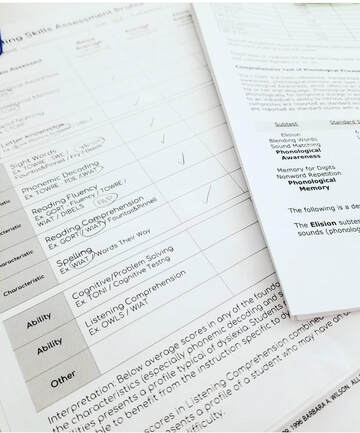
Evaluations should include an observation of the student. A student should be observed for about a fifteen minute time period. Observations should be performed during the content that is the area of the disability.
Evaluators should also observe student behavior during testing. For example, did the student appear anxious during reading subtests? Did the student use strategy for solving difficult problems, or did s/he not employ any strategies for solutions? Did the student wear glasses?
Next, provide a brief blurb that summarizes the standardized academic achievement test used to measure previously learned skills. For example, common tests are the WIAT-III, Woodcock Johnson IV Tests of Achievement, KTEA-3, etc.
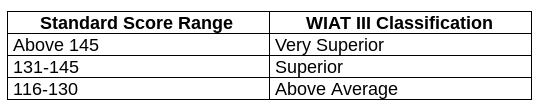
After the blurb, testers should include the standard score range along with the test’s classification. For example…
The next step is to look at each academic cluster that was tested. The tester should summarize the facilitation and purpose of each subtest. For example, the student was given two minutes to solve single-digit multiplication problems to measure fluency of basic math facts. After an evaluator summarizes a student’s performance on each subtest in a skill area, strengths and weaknesses within the cluster should be discussed. Begin with areas of strength in a student’s cluster area profile. Analyze all subtests in the skill area in order to identify strengths. Cite specific examples within the report as well to support the claims. Next, address a student’s areas of need, and use this terminology. Lagging skills should not be termed weaknesses for the word’s connotations. Again, cite specific examples to support analysis claims. Include each cluster area evaluated in the same manner.
Then, an evaluator should include additional academic testing areas. Report about these in the same manner as well, addressing areas of strength and need.
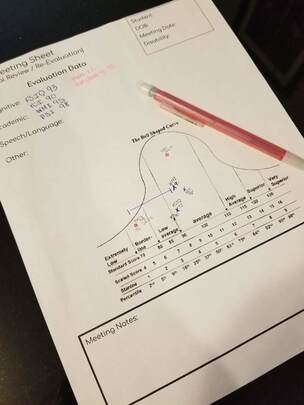
Curriculum-based measures and progress monitoring results should be reported next. Academic evaluation reports should conclude with a summary and recommendations based upon the summary. An evaluator will want to summarize the results… STUDENT has learned a strategy of using context clues in order to make meaning within a text. This was seen in the Quick Phonics Screener as well as the Reading Comprehension subtest on the WIAT-III. He has a good grasp on short vowels and consonant letter sounds and is able to apply these skills when decoding. Noted areas of need for STUDENT were long vowel words, R-controlled vowels, and consonant digraphs (i.e. wr, sl). This was seen both in the Quick Phonics Screener, WIAT-III reading subtests, as well as the Ekwall Shanker Phonics subtest. STUDENT scored in the below average range on each reading subtest in the WIAT-III. This appears to be the result of a weakness in phonological awareness. These findings were further supported by the subtests of the CTOPP. STUDENT exhibited an area of need when asked to omit a part of a given word. This shows a weakness in an awareness of and access of oral language, which is represented in written language. A deficit in phonological awareness would indicate a reading disability.
Recommendations should be listed based upon the results of the testing (i.e. the summary!). Eligibility and additional recommendations will be discussed at the student’s upcoming Team meeting when all evaluation results are reviewed. A similar statement should be included on the report.
For example… 1. Continue to teach STUDENT decoding skills/strategies in order to increase his independent application of these learned skills. 2. STUDENT should receive direct instruction in decoding long vowel words as well as words including consonant digraphs. This should be taught first in isolation, and then, STUDENT should be given the chance to apply learned skills in the context of text at his instructional level. 3. STUDENT should be explicitly taught how to establish sound/symbol relationships of all phonemes in order to improve his phonological awareness skills. 4. Additional recommendations will be made at team meeting.
Testing reports should contain a statement on validity of testing. For example, an evaluator may state, “It is felt that the results of the testing are an accurate measure of current level of academic achievement” if the evaluator believes this test to be a valid measure of performance.
And finally, give yourself some credit! Put your name, qualification(s), and job title on the report along with the date. Evaluation reports should include a tester’s signature.
Oh, and you can breathe now! :) Testing templates can be very useful as well, and they definitely help. You can grab my WIAT-IV report template, my Woodcock Johnson IV report template, or my report template bundle with the GORT-5, CTOPP-2, KeyMath, and more! Happy & Healthy Teaching! Miss Rae Related Teacher Tools...Learn more...
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
CategoriesAll 504 Academic Testing Academic Testing Reports Achievement Testing Reports Back To School B/d Reversals Coronavirus COVID-19 Discrepancy Model Distance Learning Distance Learning With LD ELL Emotional Disability Executive Functioning Extended School Year First Year Special Education Teacher Advice Fluid Reasoning FREEBIES Goal Tracking IEP IEP At A Glance IEP Goals IEP Meetings Learning Disability Oral Reading Fluency Positive Affirmations For Special Education Students Progress Monitoring Reading Remote Learning RTI Rubrics Running Records SEL For Learning Disabilities Social Emotional Learning Special Ed Teacher Interview Questions Special Ed Teacher Job Description Special Education Special Education Progress Reports Special Education Reading Special Education Reading Programs Special Education Students Special Education Teachers Special Education Teachers Positive Affirmations Special Education Teacher Tips Special Education Websites Specially Designed Reading Instruction Teaching Strategy Trauma Wilson Reading Wilson Reading IEP Goals Writer's Workshop |




























 RSS Feed
RSS Feed